Introduction of Lime Slaking System
Lime slaking is a crucial process in various industries, particularly in water treatment, environmental management, and chemical manufacturing. The process involves the conversion of quicklime (calcium oxide) into hydrated lime (calcium hydroxide) by reacting it with water. This transformation is essential for achieving the desired chemical properties and applications of lime in various fields. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of lime slaking systems, including the equipment involved, the process flow, and the performance and applications of the resulting hydrated lime.
The Lime Slaking Process system
The lime-slaking process can be divided into several key steps:
- Raw Material Preparation: The first step involves procuring quicklime, which is usually produced by heating limestone (calcium carbonate) in a kiln at high temperatures (around 900-1000°C). The resulting quicklime is a dry, powdery substance.
- Slaking Reaction: The core of the lime slaking process is the reaction of quicklime with water. The reaction is exothermic, producing heat and hydrated lime: [
CaO + H_2O \rightarrow Ca(OH)_2 + Heat
] This reaction produces calcium hydroxide, which is commonly referred to as slaked lime or hydrated lime. - Cooling and Separation: The heat generated during the slaking process can elevate the temperature of the slaked lime slurry. Therefore, cooling systems may be employed to ensure that the temperature remains within safe limits for subsequent processing. Additionally, any unreacted quicklime particles may need to be separated from the hydrated lime.
- Storage and Handling: Once slaked, the hydrated lime is usually in the form of a slurry, which can be stored in tanks or silos. Proper handling procedures must be followed to prevent dust formation and ensure safety.
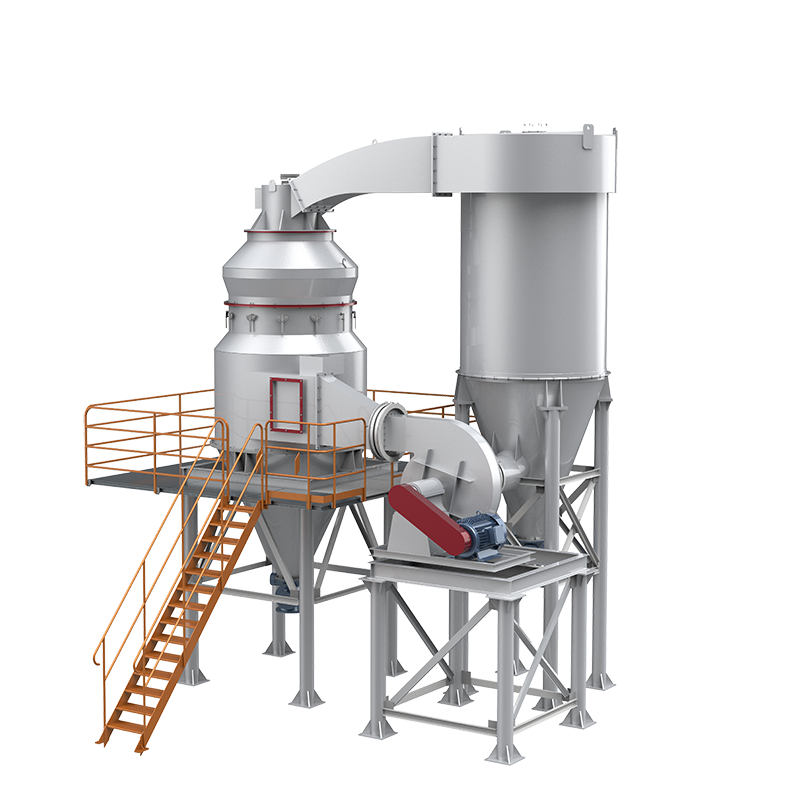
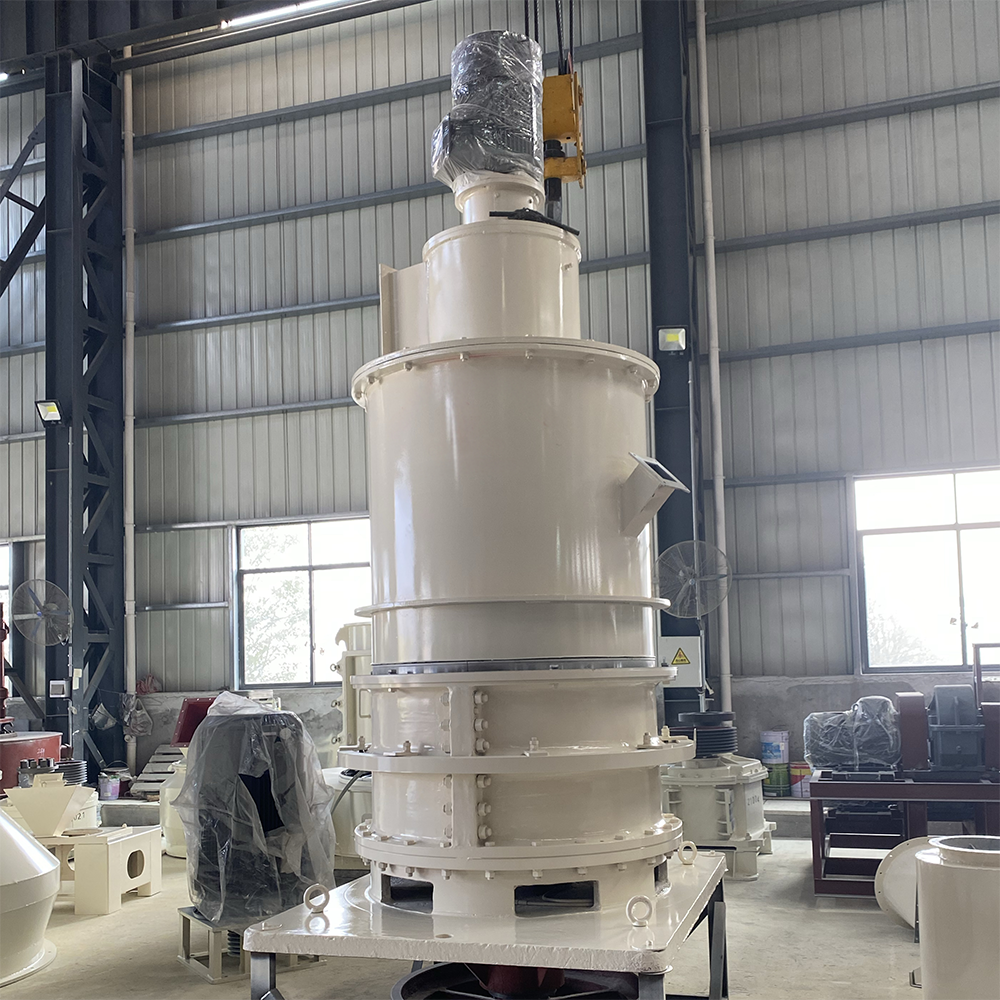
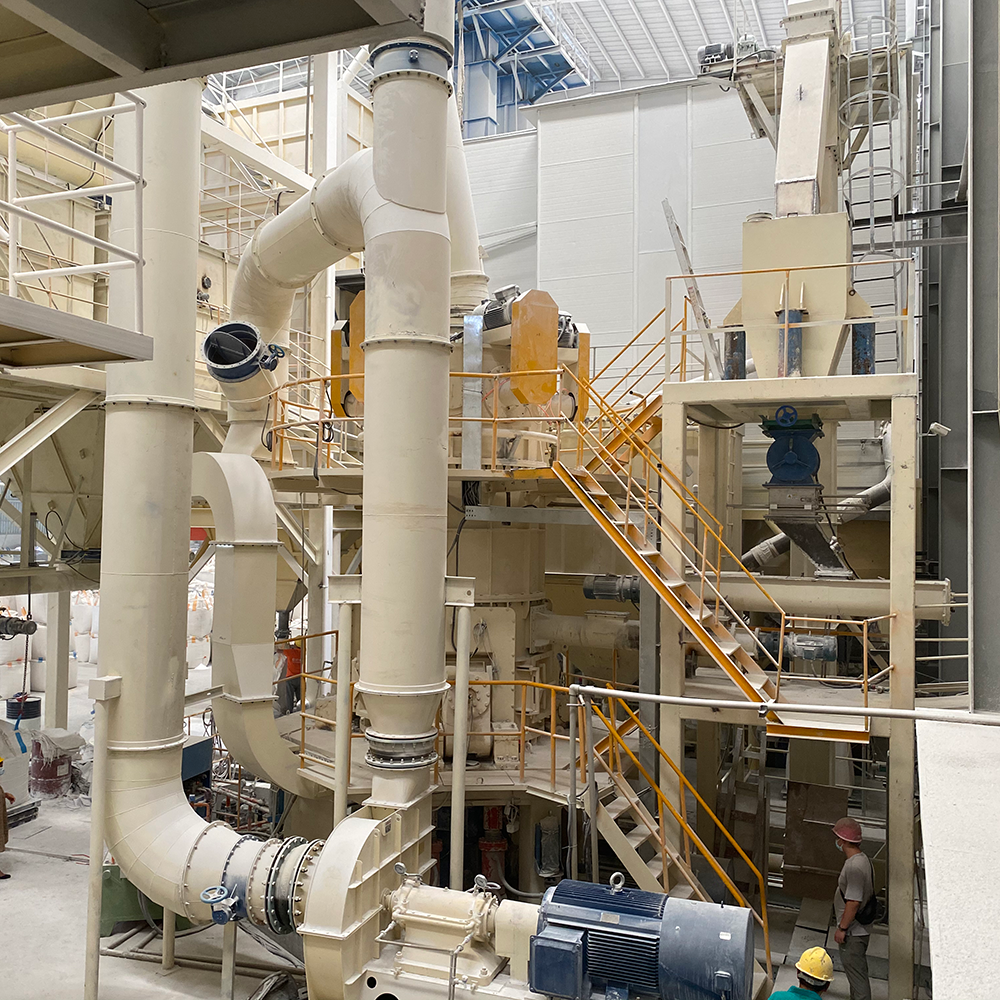
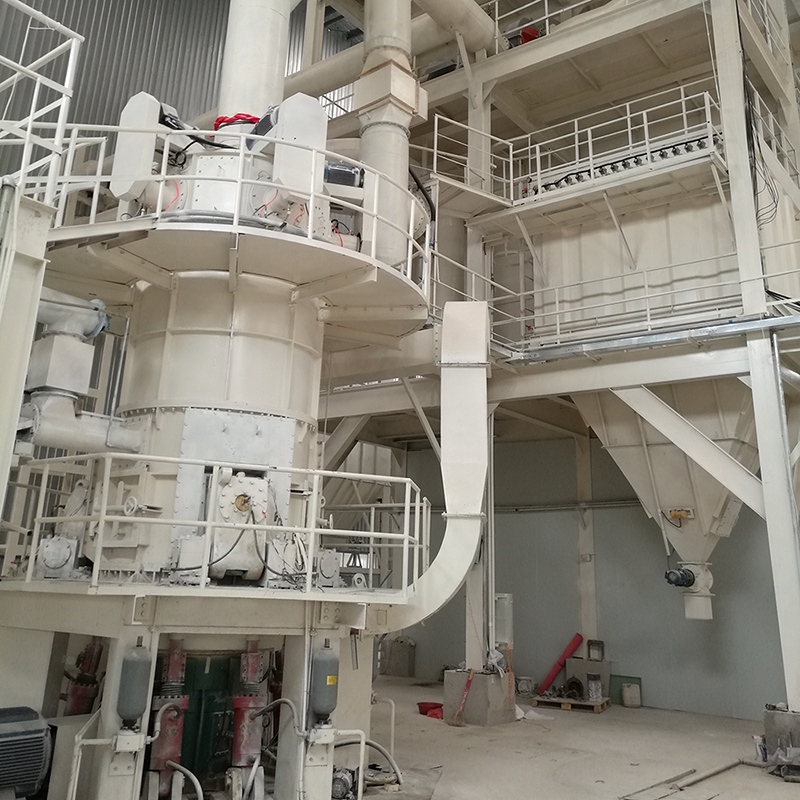
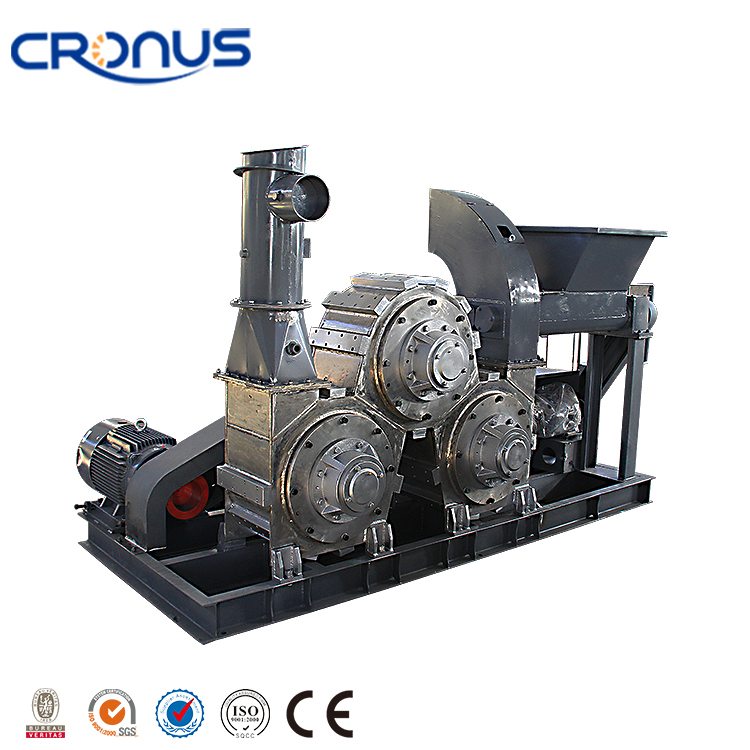
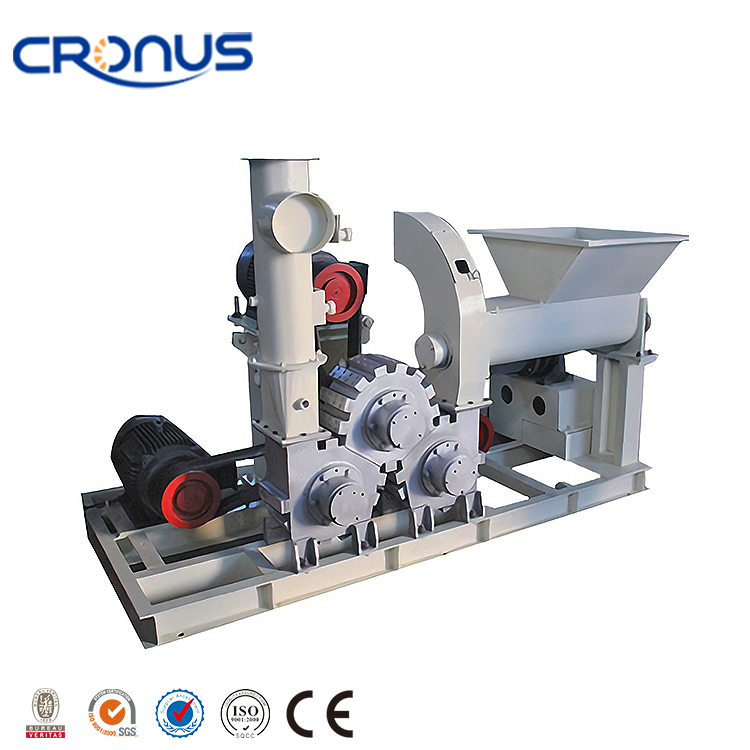
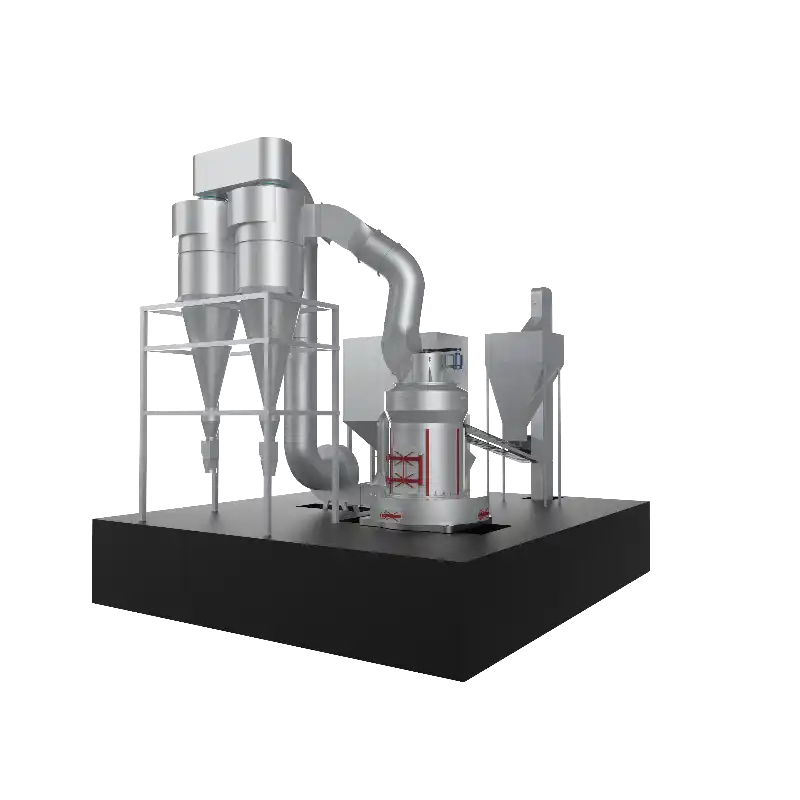
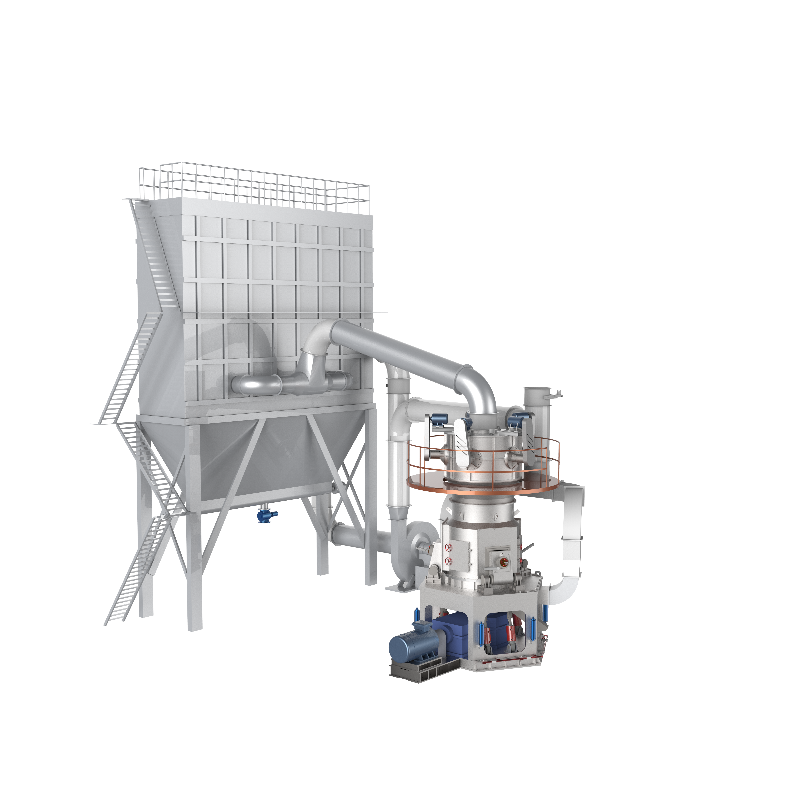
Equipment Used in Lime Slaking Systems
A lime-slaking system typically consists of several key pieces of equipment:
- Quicklime Storage Silos: These structures store quicklime before it is fed into the slaking system. They are designed to avoid moisture ingress and ensure a steady supply of raw material.
- Slaking Tanks: The heart of the slaking system, slaking tanks mix quicklime with water. These tanks are often equipped with mechanical agitators to ensure thorough mixing and prevent the formation of clumps.
- Hydrated Lime Slurry Pumps: Once the slaking reaction is complete, the hydrated lime slurry is transferred to storage or processing units using pumps designed for slurries. These pumps are essential for maintaining the flow and ensuring consistent delivery of hydrated lime.
- Cooling Systems: As the slaking process is exothermic, cooling systems such as heat exchangers may be included in the setup to dissipate excess heat and prevent overheating.
- Filtration Units: To ensure high-quality hydrated lime, filtration units may be incorporated to remove any residual quicklime particles or impurities.
- Storage Tanks for Hydrated Lime: After processing, the slaked lime is stored in large tanks. These tanks should be designed to maintain the stability of the hydrated lime slurry and prevent settling.
- Dust Control Systems: Given that lime can create dust when handled, dust control systems, including baghouses or scrubbers, are vital to maintaining air quality and ensuring worker safety.
Process Flow of Lime Slaking
A typical lime slaking process flow can be illustrated as follows:
- Input of Quicklime: Quicklime is fed from storage silos into the slaking tank.
- Water Addition: Water is added to the slaking tank, often via a controlled flow system to ensure the correct ratio of water to quicklime.
- Slaking Reaction: The quicklime and water interact in the slaking tank, where mechanical stirring facilitates the reaction.
- Cooling: If necessary, the slurry is cooled to maintain optimal processing temperatures.
- Separation and Filtration: Any unreacted quicklime is separated and filtered out.
- Storage: The hydrated lime slurry is pumped into storage tanks for further use or distribution.
Performance and Properties of Hydrated Lime
Hydrated lime produced through the slaking process exhibits several favorable properties:
- High Reactivity: Hydrated lime is highly reactive and can readily participate in various chemical reactions, making it ideal for applications in waste treatment and neutralization processes.
- pH Control: Due to its alkaline nature, hydrated lime is effective in adjusting the pH of solutions, which is critical in water treatment and soil stabilization applications.
- Flocculation Agent: Hydrated lime can act as a flocculating agent in water treatment, helping to aggregate and remove suspended particles from water.
- Safe Handling: Compared to quicklime, hydrated lime is safer to handle, as it is less caustic and has a lower risk of causing chemical burns.
Applications of Hydrated Lime
Hydrated lime has a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Water Treatment: It is extensively used in municipal water treatment plants to precipitate heavy metals and adjust pH levels, ensuring safe drinking water.
- Soil Stabilization: In construction and civil engineering, hydrated lime is used to improve soil properties and enhance the performance of road bases and stabilizing soils for foundations.
- Environmental Remediation: Hydrated lime plays a crucial role in the treatment of industrial wastewater and the neutralization of acidic soils, effectively reducing environmental pollution.
- Chemical Manufacturing: It is a key reagent in the production of various chemicals, including calcium sulfite in flue gas desulfurization processes.
- Food Industry: Hydrated lime is used in the food industry for processes like water purification and as a food additive for certain applications.
- Pulp and Paper Industry: It is employed in the pulping process to remove lignin from wood, contributing to the production of paper products.
Conclusion
A lime slaking system is a vital component in various industrial processes, enabling the efficient conversion of quicklime into hydrated lime. The equipment involved in this system, including slaking tanks, pumps, and storage facilities, plays a critical role in ensuring the effectiveness and safety of the process. Hydrated lime's unique properties and versatility make it a valuable material in water treatment, soil stabilization, environmental remediation, and chemical manufacturing. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for high-quality hydrated lime and efficient lime slaking systems will remain strong, underscoring the importance of this process in modern industrial applications.