In modern agriculture and horticulture, lime has become an important material for improving the plant growth environment due to its unique chemical and physical properties. Its benefits to plants are reflected in many key aspects, from soil improvement to pest and disease control, ensuring the healthy growth of plants.

Adjust soil pH to create a high-quality growth environment
The pH value of soil is crucial to plant growth. When the soil is too acidic (pH value is lower than 5.5), essential nutrients such as iron and magnesium will be fixed in large quantities, resulting in the inability of plants to absorb them normally, leading to poor growth. Lime is like a "soil pH regulator", which significantly increases the soil pH value by neutralizing acidic substances in the soil. Among them, agricultural lime (calcium carbonate) is a commonly used soil acidity improver, which can effectively alleviate soil acidity problems, create a suitable nutrient absorption environment for plant roots, and ultimately achieve an increase in crop yields.
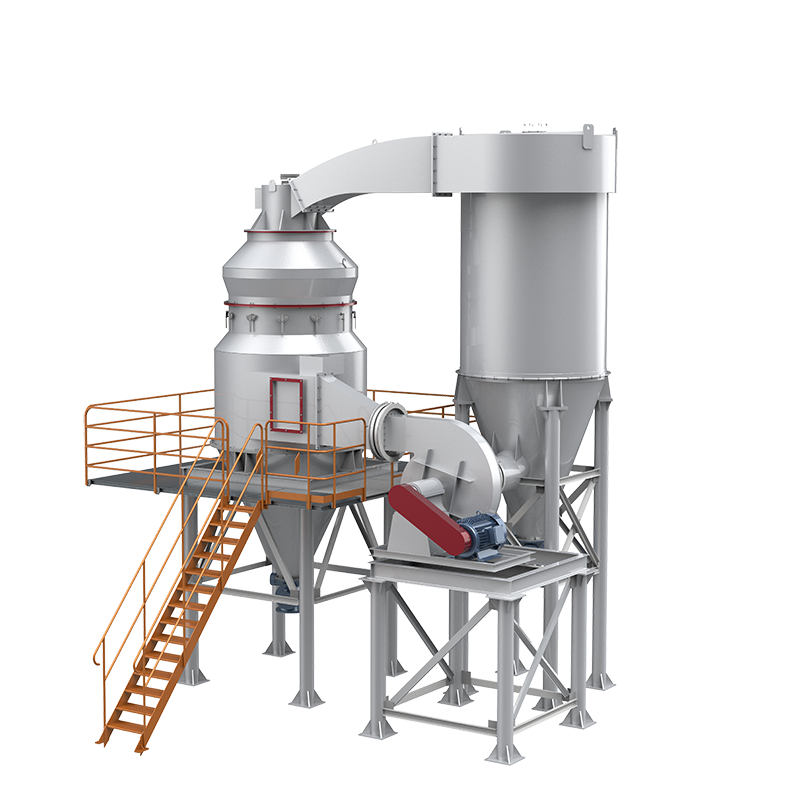
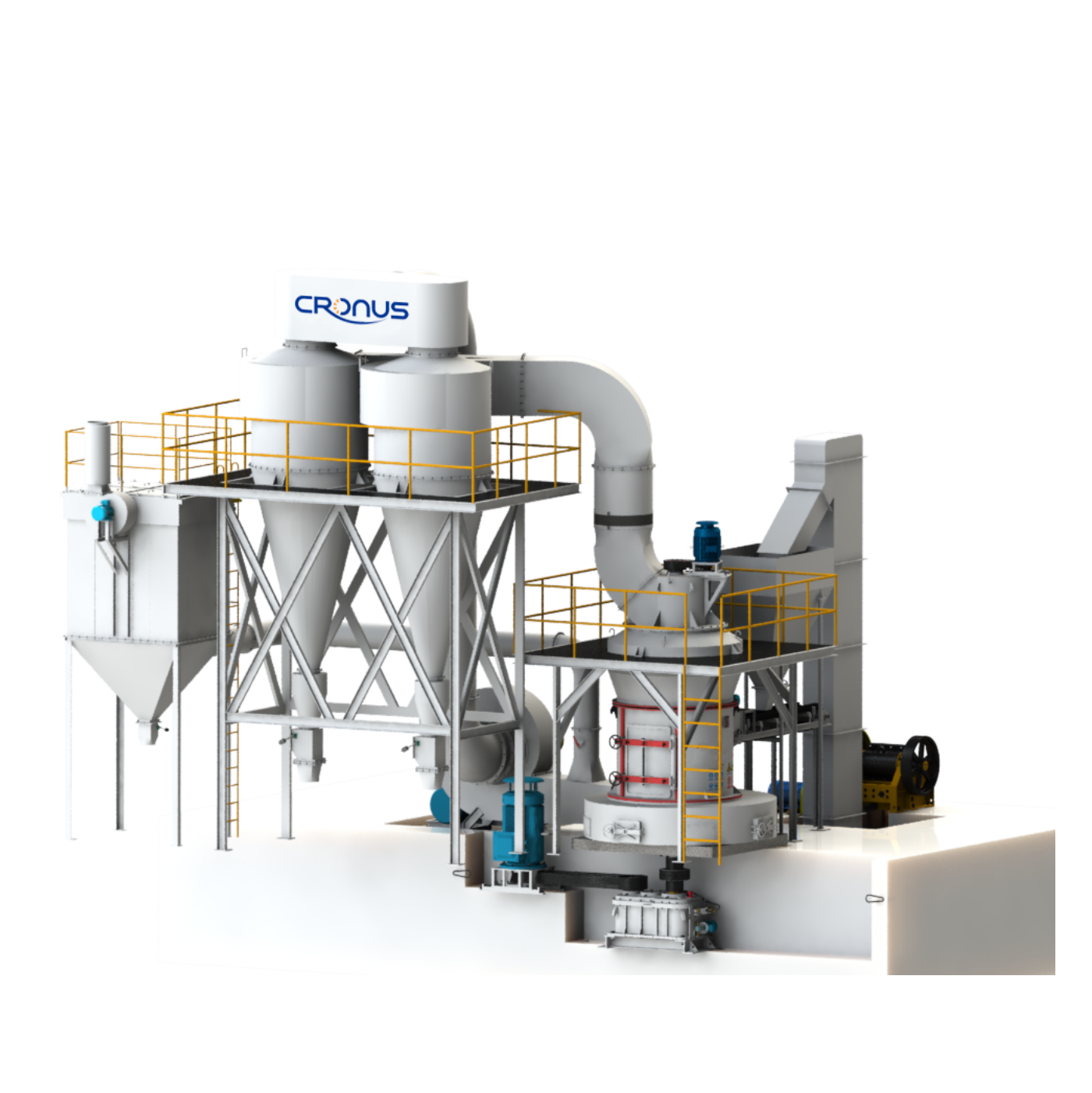
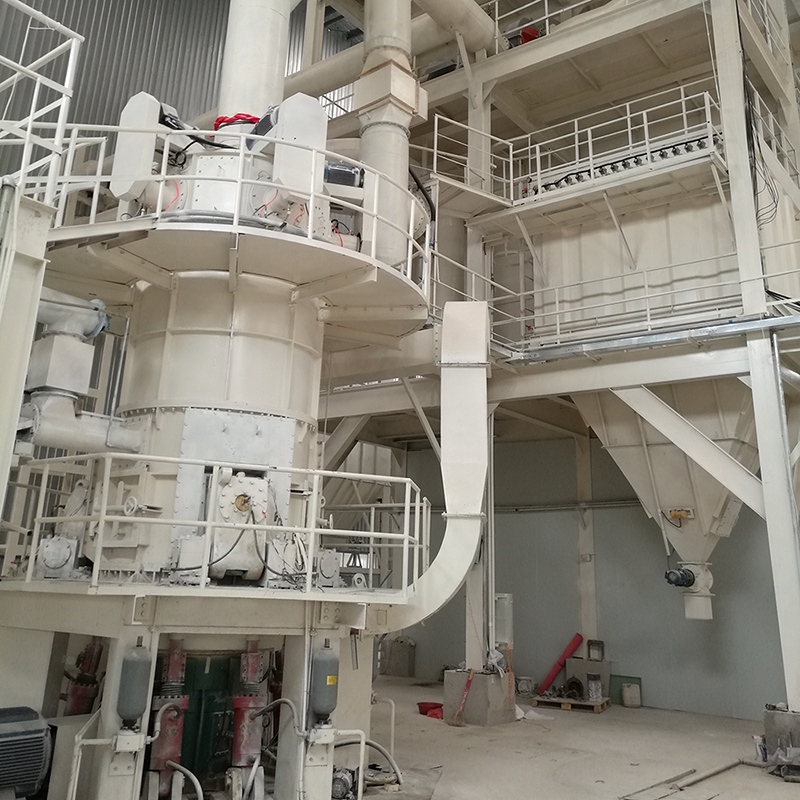
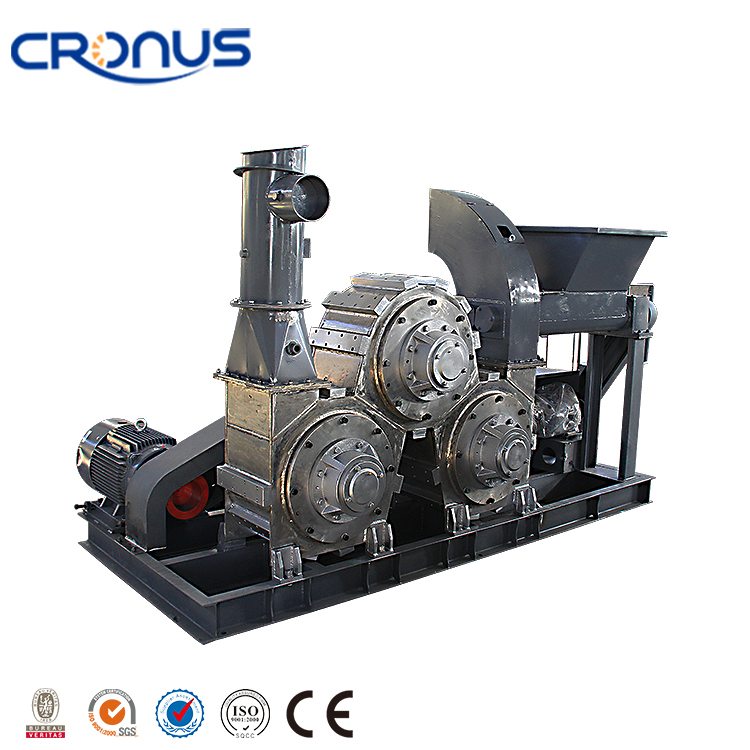
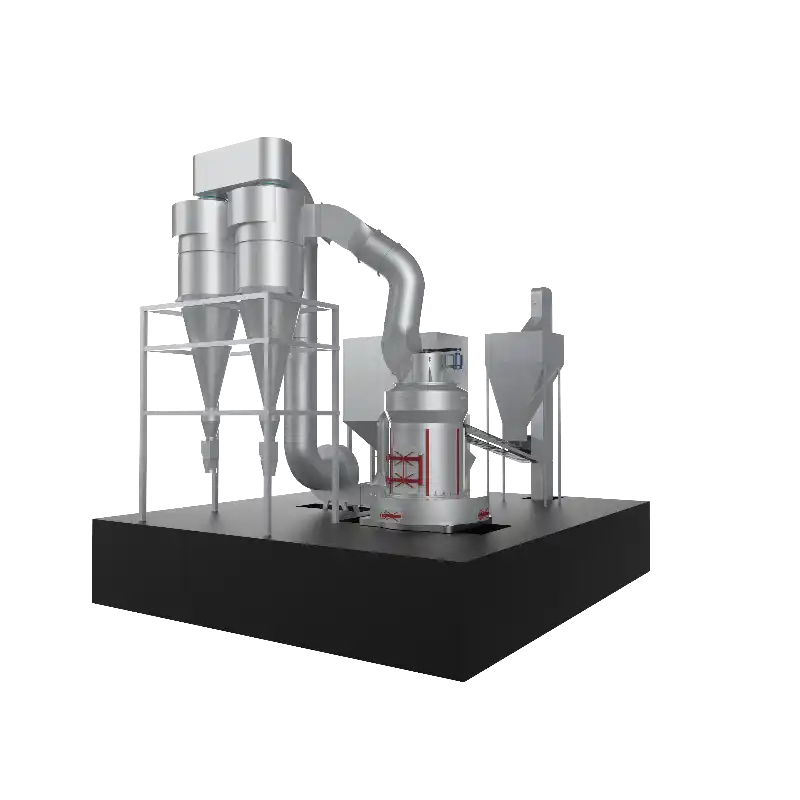
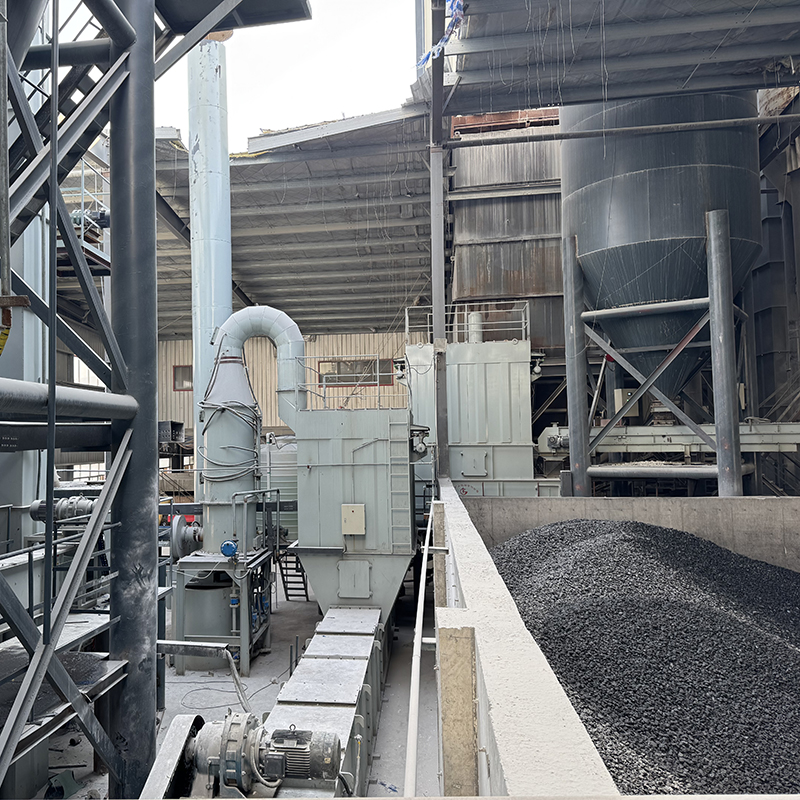
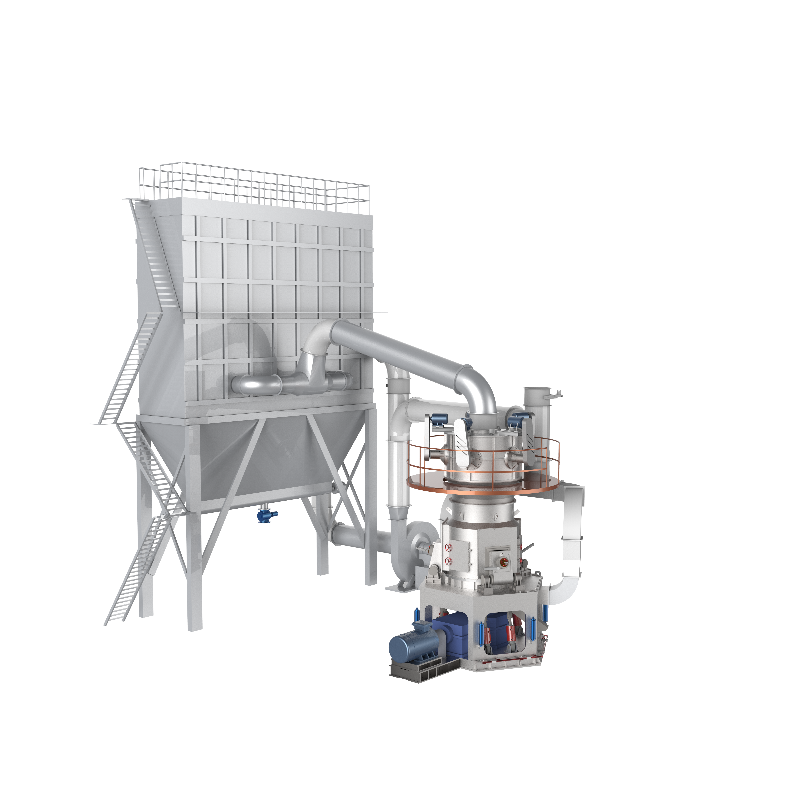
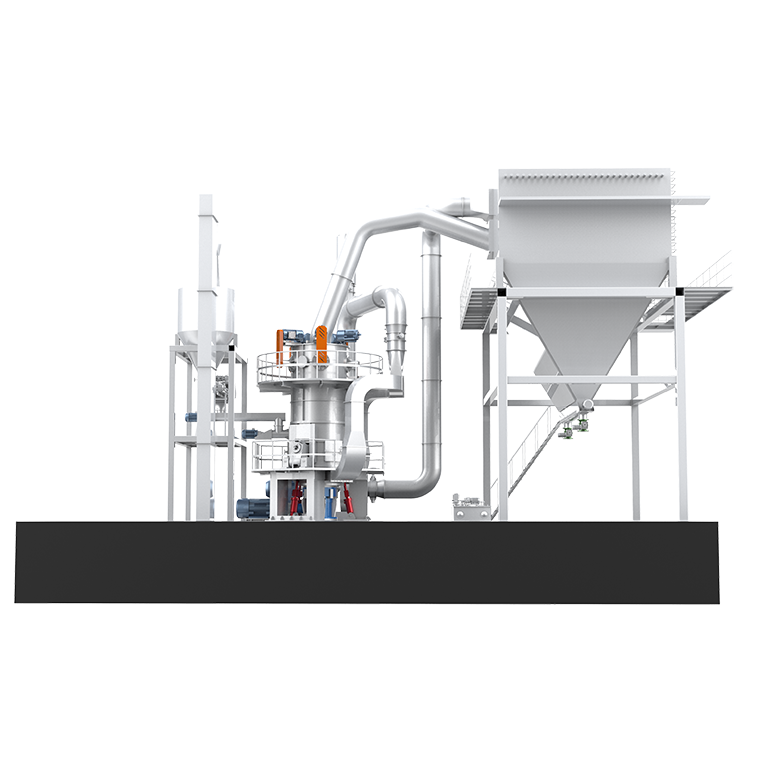
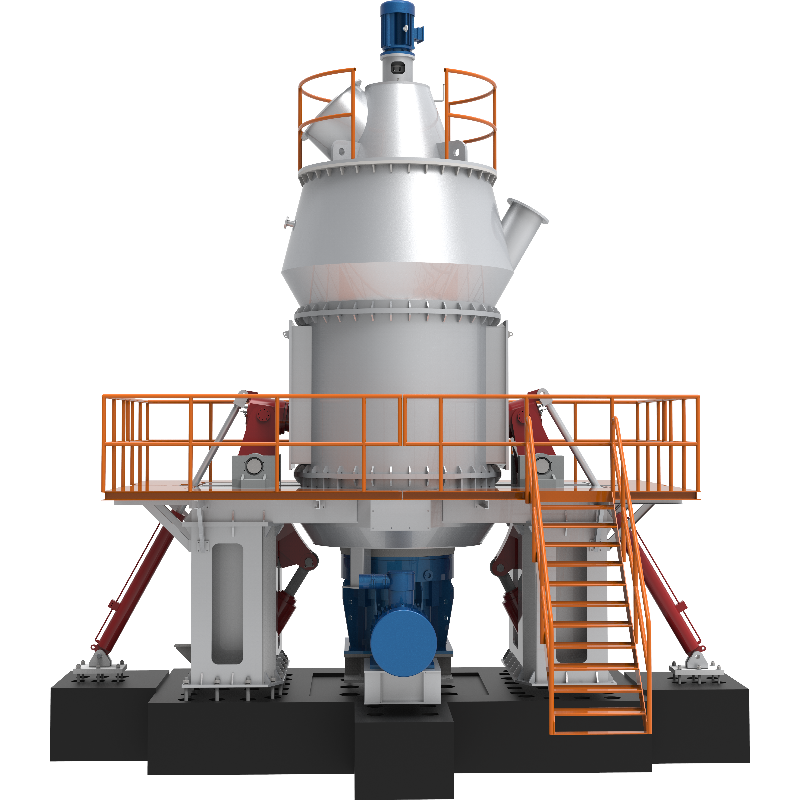
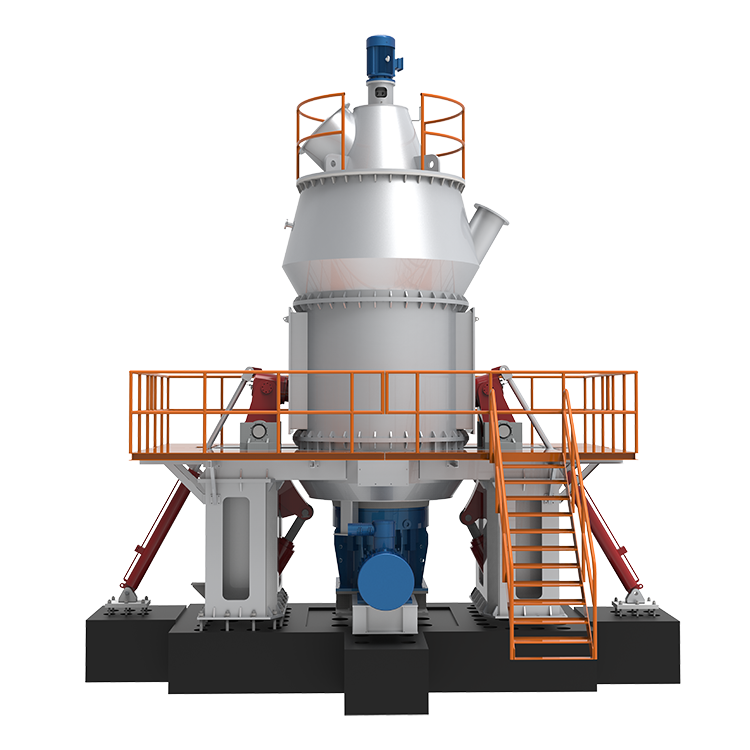
CRSH Lime Slaking System
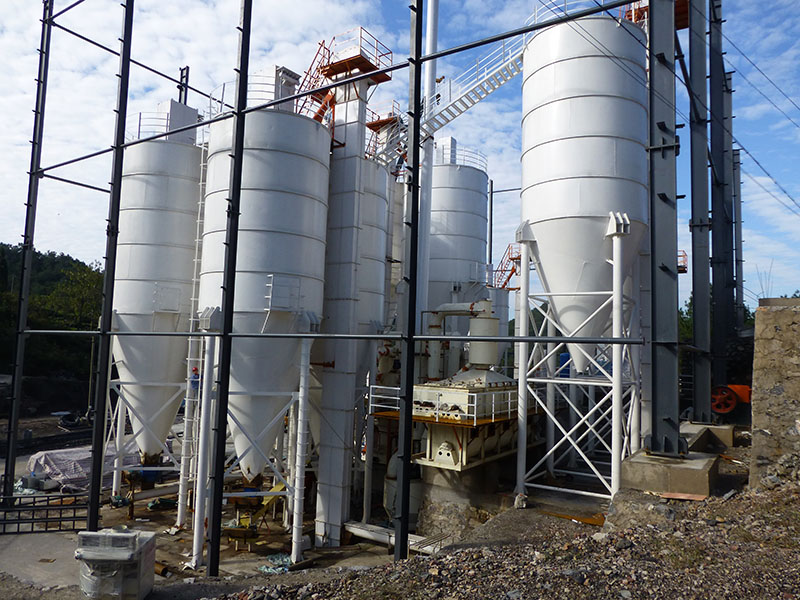
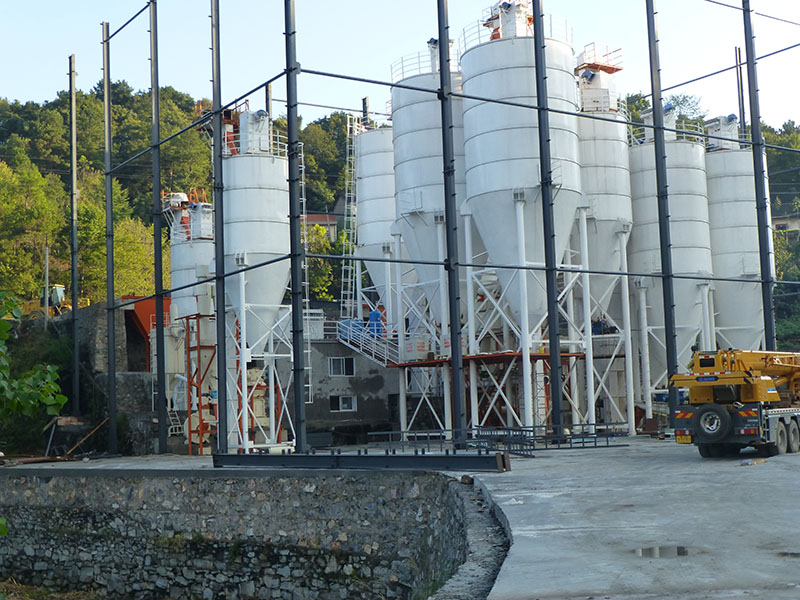


Supplement calcium and magnesium elements to lay a solid foundation for plant growth
Calcium and magnesium are important nutrients that are indispensable for plant growth. Lime is rich in these two elements, providing strong support for the healthy growth of plants. Calcium participates in the construction and maintenance of plant cell walls, enhancing the strength and stability of cell walls and making plant stems tougher and more upright; magnesium, as a core component of chlorophyll, directly affects the efficiency of photosynthesis. Sufficient magnesium can ensure that plants can efficiently convert light energy into chemical energy and promote the healthy growth of plants. Quicklime (calcium oxide) and slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) are both high-quality sources of calcium and magnesium minerals.
Optimize soil structure and help roots flourish
The effect of lime on improving soil physical properties cannot be underestimated. It can effectively improve soil aeration and water retention, increase soil porosity, break soil compaction, and reduce compaction. In such a loose and breathable soil environment, plant roots can stretch freely and absorb water and nutrients in the soil more easily. In addition, lime can also improve soil drainage, prevent water accumulation from causing plant root rot, and create a healthy living space for root growth.
Play a bactericidal effect and resist the invasion of pests and diseases
Lime has a strong bactericidal and disinfecting ability and is a natural barrier for plants to resist pathogens and pests. Bordeaux liquid made from quicklime is a widely used high-efficiency fungicide that can effectively inhibit the occurrence of a variety of plant diseases, such as grape downy mildew and apple anthracnose. Spreading lime in planting areas such as orchards and vegetable gardens can also reduce the number of harmful pathogens and eggs in the soil and reduce the risk of outbreaks of pests and diseases.
Improve fertilizer efficiency and promote efficient nutrient utilization
Lime can significantly improve the effectiveness of nutrients in the soil, especially the utilization rate of phosphorus and nitrogen. It can promote the mineralization process of phosphorus in the soil, convert phosphorus elements that are difficult to be absorbed by plants into usable forms, allow nutrients in fertilizers to be better absorbed by plants, reduce fertilizer waste, and improve fertilization efficiency.
Reduce metal toxicity and protect plant health and safety
In acidic soils, metal elements such as aluminum and iron exist in the form of highly toxic ions, causing serious damage to plants. Lime neutralizes soil acidity, reduces the activity of these harmful metal ions, alleviates their toxic effects on plant roots and above-ground parts, and provides a safe soil environment for plant growth.
Activate microbial vitality and enhance soil ecological functions
Lime can optimize the soil environment and create favorable conditions for the growth and reproduction of beneficial microorganisms. With the help of lime, these microorganisms accelerate the mineralization and decomposition of organic matter in the soil and convert complex organic matter into nutrients that are easily absorbed by plants. For example, lime can enhance the activity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, convert nitrogen in the air into nitrogen that can be used by plants, improve soil fertility, and form a benign soil ecological cycle.
Diverse application scenarios, expanding the boundaries of agriculture and horticulture
Lime is widely used in horticulture and agriculture. In addition to the above main functions, it can also be used to make herbicides, disinfectants, etc.; in industrial production and construction, lime is also an indispensable and important raw material.
Although lime has many benefits for plant growth, scientific and reasonable application is essential. Different soil types and crop needs have specific requirements for the amount and method of lime application. For example, clay with strong acidity requires more lime than sandy soil; tea trees that like acidity should not use lime.
In practical applications, precise proportioning is required based on soil test results and crop characteristics to avoid soil alkalinization due to excessive application, give full play to the positive role of lime in plant growth, and achieve sustainable development of agricultural and horticultural production.